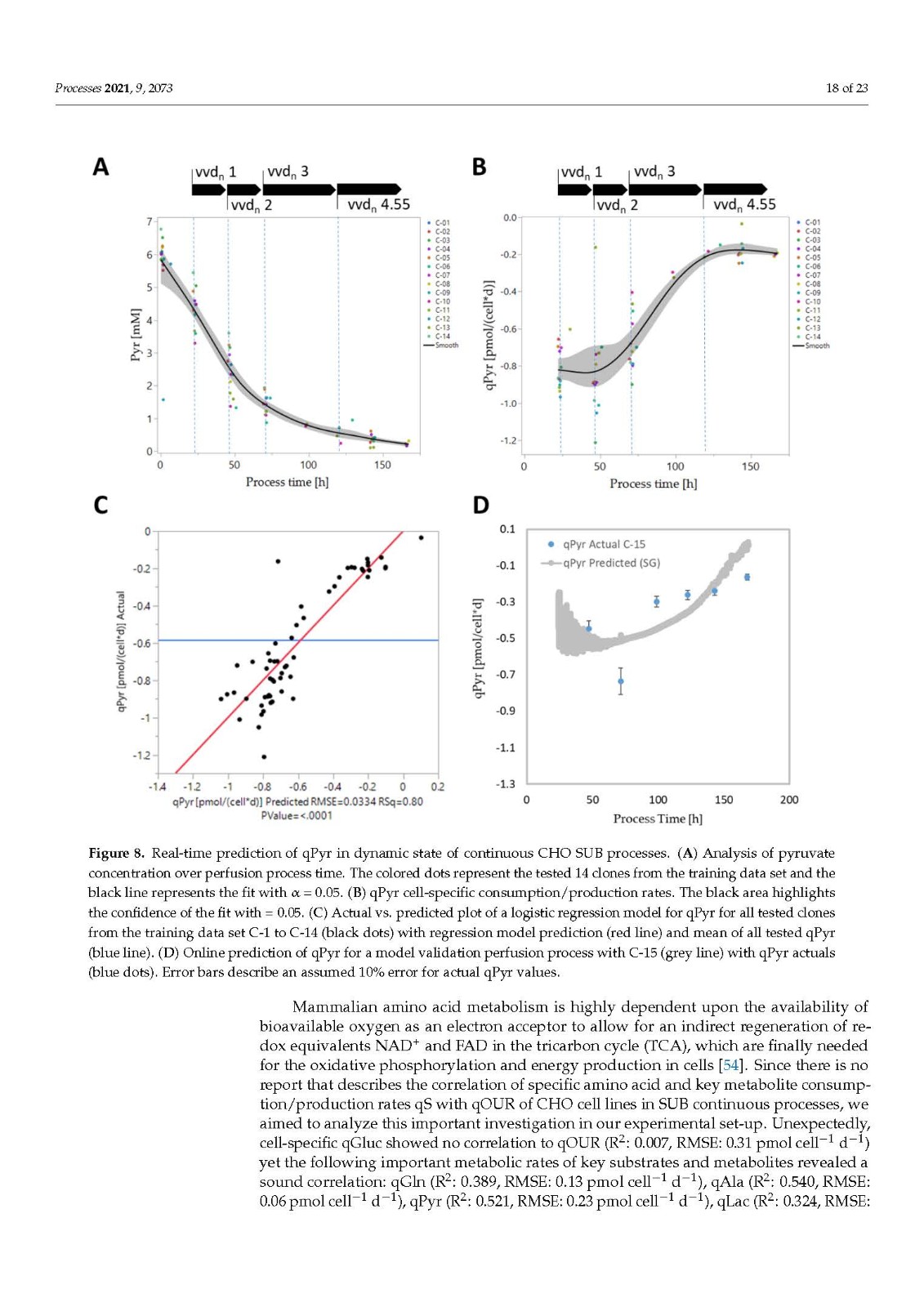
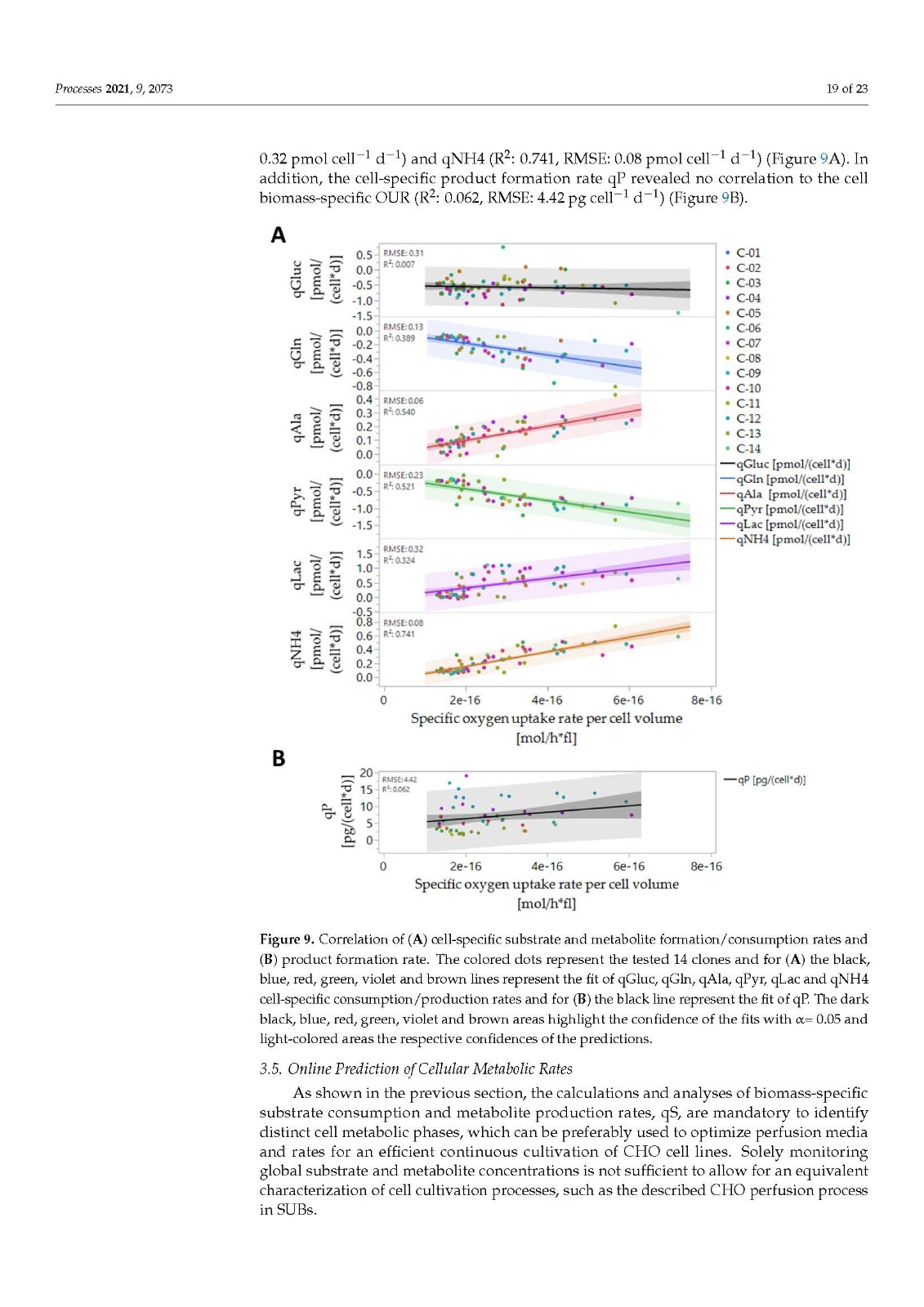
In mammalian cell culture, especially in pharmaceutical manufacturing and research, biomass and metabolic monitoring are mandatory for various cell culture process steps to develop and, finally, control bioprocesses. As a common measure for biomass, the viable cell density (VCD) or the viable cell volume (VCV) is widely used. This study highlights, for the first time, the advantages of using VCV instead of VCD as a biomass depiction in combination with an oxygen-uptake- rate (OUR)-based soft sensor for real-time biomass estimation and process control in single-use bioreactor (SUBs) continuous processes with Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell lines. We investigated a series of 14 technically similar continuous SUB processes, where the same process conditions but different expressing CHO cell lines were used, with respect to biomass growth and oxygen demand to calibrate our model. In addition, we analyzed the key metabolism of the CHO cells in SUB perfusion processes by exometabolomic approaches, highlighting the importance of cell-specific substrate and metabolite consumption and production rate qS analysis to identify distinct metabolic phases. Cell-specific rates for classical mammalian cell culture key substrates and metabolites in CHO perfusion processes showed a good correlation to qOUR, yet, unexpectedly, not for qGluc. Here, we present the soft-sensoring methodology we developed for qPyr to allow for the real-time approximation of cellular metabolism and usage for subsequent, in-depth process monitoring, characterization and optimization.

细胞转瓶2L
在哺乳动物细胞培养中,尤其是在药物制造和研究中,生物量和代谢监测对于开发和最终控制生物过程的各种细胞培养过程步骤是必不可少的。作为生物量的常用度量,活细胞密度 (VCD) 或活细胞体积 (VCV) 被广泛使用。本研究首次强调了使用 VCV 代替 VCD 作为生物量描述的优势,结合基于吸氧率 (OUR) 的软传感器,用于实时生物量估算和一次性过程控制中国仓鼠卵巢 (CHO) 细胞系的生物反应器 (SUB) 连续过程。我们研究了一系列 14 个技术上相似的连续 SUB 工艺,其中使用了相同的工艺条件但使用了不同的表达 CHO 细胞系,关于生物量增长和需氧量来校准我们的模型。此外,我们通过外代谢组学方法分析了 SUB 灌注过程中 CHO 细胞的关键代谢,强调了细胞特异性底物和代谢物消耗以及生产率 qS 分析对识别不同代谢阶段的重要性。CHO 灌注过程中经典哺乳动物细胞培养关键底物和代谢物的细胞特异性速率显示出与 qOUR 的良好相关性,但出人意料的是,与 qGluc 无关。在这里,我们介绍了我们为 qPyr 开发的软传感方法,以允许实时近似细胞代谢和使用情况,以便进行后续深入的过程监测、表征和优化。我们通过外代谢组学方法分析了 SUB 灌注过程中 CHO 细胞的关键代谢,强调了细胞特异性底物和代谢物消耗以及生产率 qS 分析对识别不同代谢阶段的重要性。CHO 灌注过程中经典哺乳动物细胞培养关键底物和代谢物的细胞特异性速率显示出与 qOUR 的良好相关性,但出人意料的是,与 qGluc 无关。在这里,我们介绍了我们为 qPyr 开发的软传感方法,以允许实时近似细胞代谢和使用情况,以便进行后续深入的过程监测、表征和优化。我们通过外代谢组学方法分析了 SUB 灌注过程中 CHO 细胞的关键代谢,强调了细胞特异性底物和代谢物消耗以及生产率 qS 分析对识别不同代谢阶段的重要性。CHO 灌注过程中经典哺乳动物细胞培养关键底物和代谢物的细胞特异性速率显示出与 qOUR 的良好相关性,但出人意料的是,与 qGluc 无关。在这里,我们介绍了我们为 qPyr 开发的软传感方法,以允许实时近似细胞代谢和使用情况,以便进行后续深入的过程监测、表征和优化。强调细胞特异性底物和代谢物消耗和生产率 qS 分析的重要性,以确定不同的代谢阶段。CHO 灌注过程中经典哺乳动物细胞培养关键底物和代谢物的细胞特异性速率显示出与 qOUR 的良好相关性,但出人意料的是,与 qGluc 无关。在这里,我们介绍了我们为 qPyr 开发的软传感方法,以允许实时近似细胞代谢和使用情况,以便进行后续深入的过程监测、表征和优化。强调细胞特异性底物和代谢物消耗和生产率 qS 分析的重要性,以确定不同的代谢阶段。CHO 灌注过程中经典哺乳动物细胞培养关键底物和代谢物的细胞特异性速率显示出与 qOUR 的良好相关性,但出人意料的是,与 qGluc 无关。在这里,我们介绍了我们为 qPyr 开发的软传感方法,以允许实时近似细胞代谢和使用情况,以便进行后续深入的过程监测、表征和优化。
Our data also demonstrated that higher model accuracy was established when VCV instead of VCD was used as biomass depiction. This strengthens our strong belief in a paradigm change regarding biomass description in modern bioprocesses. VCD should no longer be the leading, or the only, measurement looked at when it comes to biomass determination. The cell size or volume, its distribution over time and, of course, the VCV should be used by default to accurately describe the biomass and all derived metabolic variables, such as mAB, lactate production rate, or glucose/oxygen consumption rates. Conclusions, based only on cell density measurements, can lead to wrong assumptions, calculations or other unforeseen misinterpretations, generating a fragmented picture of the biomass [38,40]. As modern bioprocesses can be highly complex and dynamic, the biomass and cellular metabolism analysis should be as comprehensive as possible to generate a comparable and reproducible data basis. Furthermore, the utilization of an off-gas-based soft sensor is easy to implement in SUB systems as well as in common stainless steel plants. For this purpose, the installation of any hard-type probes inside the bioreactor is not necessary and does not increase handling or decrease safety and therefore prevents possible contamination risks. The fundamental correlation of biomass growth and increasing oxygen demand can be used, optimized and extended to generate profound real-time knowledge on diverse bioprocess variables such as the shown biomass and metabolic nutrient rate soft sensor. Moreover, off-gas analysis can be used to determine the true bioreactor pH without any sampling or as non-invasive method for online pCO2 monitoring, which underlines the flexibility and outstanding character of having an off-gas analyzer implemented and running.

高效摇瓶5L
我们的数据还表明,当使用 VCV 代替 VCD 作为生物量描述时,建立了更高的模型精度。这增强了我们对现代生物过程中生物质描述范式变化的坚定信念。在生物量测定方面,VCD 不应再成为主要或唯一的测量方法。默认情况下,应使用细胞大小或体积、其随时间的分布以及 VCV 来准确描述生物量和所有衍生的代谢变量,例如 mAB、乳酸生产率或葡萄糖/氧气消耗率。仅基于细胞密度测量的结论可能会导致错误的假设、计算或其他不可预见的误解,从而生成生物量的碎片化图片。由于现代生物过程可能非常复杂和动态,生物量和细胞代谢分析应尽可能全面,以生成可比较和可重复的数据基础。此外,基于废气的软传感器的使用很容易在 SUB 系统以及普通不锈钢工厂中实施。为此,不需要在生物反应器内安装任何硬型探针,并且不会增加操作或降低安全性,因此可以防止可能的污染风险。可以使用、优化和扩展生物量增长和增加的需氧量之间的基本相关性,以生成有关各种生物过程变量的深刻实时知识,例如所示的生物量和代谢营养率软传感器。而且,监测,这强调了实施和运行废气分析仪的灵活性和突出特点。
关键词:process analytical technologies (PAT),off-gas analytic,real-time monitoring,viable cell biomass, perfusion process,continuous process,single-use bioreactor (SUB),oxygen uptake rate (OUR),soft sensor过程分析技术(PAT),废气分析,实时监控,活细胞生物量,灌注过程,连续过程,一次性生物反应器(SUB),摄氧率 (OUR),软传感器













来源:MDPI https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9717/9/11/2073/htm
上一篇: 血清瓶的瓶盖是什么材质